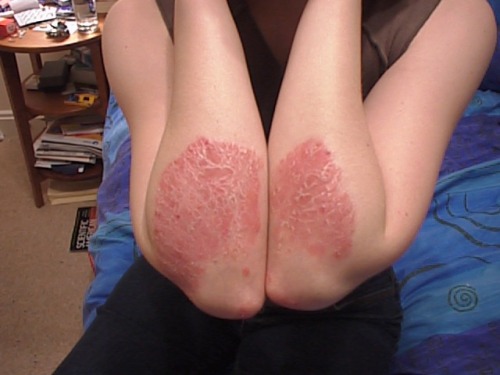
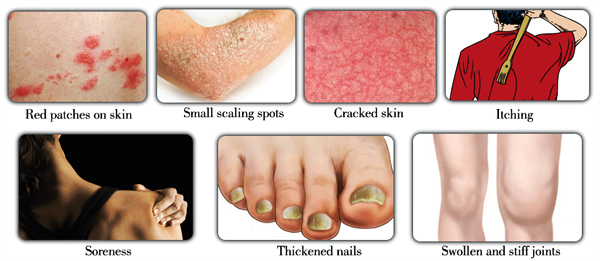
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that results in dry, flaky, inflamed white to silver patches on skin. It occurs in age group of 15-35 years.
It is characterised by the following signs and symptoms:
- The psoriatic signs and symptoms may occur with different intensities and frequencies. Psoriasis could be mild, with small patches of inflammation or rash on skin over elbows, knees or lower back. There might be thickening or presence of patches on the scalp as well.
- In case of moderate to severe psoriasis, there is inflammation with raised red patches capped with loose, silvery white, scaly skin. In severe psoriasis, the skin becomes itchy as well as tender. Sometimes large plaques form on the skin that may become uncomfortable. These plaques or large patches may cluster together and cover large region of skin, such as the entire arm or the entire back.
- In some cases, psoriasis may also result in causing swollen, tender, and painfuljoints. This is known as psoriatic arthritis. This type of arthritismay also affect fingernails as well as the toenails, causing pitting, change in color, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. This may lead tobuild up of dead skin under the nails of fingers as well as toes.
- The most common feature of psoriasis is the presence of bleeding on scraping or peeling the skin over these patches. These are called Auspitz signs.
- Itching or flare ups may be felt in the body folds like below the breasts and buttocks.
- Patients who are obese and have psoriasis are commonly predisposed to diabetes and heart diseases.
- Sometimes the psoriatic patches become tear drop shaped and are called guttate psoriasis.
- Psoriasis that occurs due to cuts, bites or burns is called Koebner’s phenomenon.
Is psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious as it does not pass from one individual to other and autoimmunity as well as genetics is the only cause of psoriasis.
Duration and frequency of Psoriasis
Symptoms of psoriasis often disappear even without treatment, and then the flare up may reappear in some time due to the triggering factors.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
Most of the times, doctors may diagnose psoriasis by simply looking at the patches on the skin, scalp, or nails. Special tests aren’t required for diagnosing psoriasis. But some of the tests that can be conducted for psoriasis include:
- Biopsy: It is a method for confirming the diagnosis of psoriasis when it is hard to differentiate by simply looking at the skin. It is performed by removing a small layer from the skin and sending it to the lab for analysis.
- Radiographs: In case of joint pain or psoriatic arthritis X-rays may be taken for the diagnostic purpose.
- Blood tests: These help in confirming the diagnosis by ruling out other forms of arthritis or skin diseases.
- Throat cultures: These are used especially if the doctor thinks that it might be a guttate psoriasis. Strep throat is the commonly used throat culture for this.
- KOH test: Sometimes potassium hydroxide skin test is done in order to rule out any sort of fungal infection of skin.