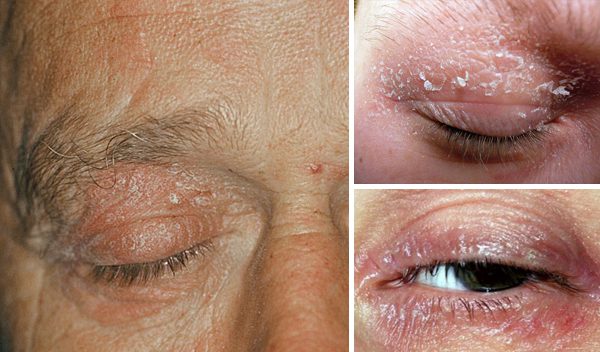
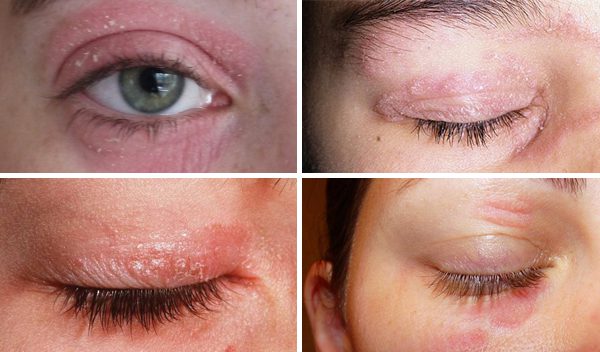
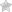Psoriasis on the eyelids is a chronic inflammatory and proliferative condition with an autoimmune background. The most characteristic for a histopathological picture is excessive accelerated keratosis with red papules covered with silvery-white scales.
Symptoms
Typical symptoms of psoriasis are inflammatory erythematous, scaly skin, the disease is often accompanied by itching and burning. There may be painful cracks in the affected parts of the epidermis. Depending on the severity, doctors define two types of psoriasis:
- A soft form, when less than ten percent of the skin surface is affected.
- A moderate and severe form about which dermatologists speak, when more than 10 percent of the epidermal area is affected.
The first rashes usually have the character of small, but numerous changes, scattered on the eyelid. The areas affected by the disease are relatively clearly delineated.
The disease is included in psychosomatic disorders caused by stressful conditions and associated with stress.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist, who focuses on the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history and some rather characteristic symptoms:
- Symptom of stearin stain: scales easily removed, forming areas similar to a wax candle.
- The phenomenon of the terminal layer: with further scratching, thin, inflamed skin is visible.
- Symptom of pinpoint hemorrhages: after removal of the layer, local bleeding occurs.
In rare cases it is necessary to conduct a tissue examination (biopsy) for accurate diagnosis in order to differentiate psoriasis on a century with other inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Treatment
Psoriasis is a chronic disease for a century, and fighting with it requires that the patient be disciplined, consistent, lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid colds, excessive fatigue with regular examination at the dentist and oculist. The choice of method of treatment depends on the severity of the lesions of the century, the subclinical variation of psoriasis, the age of the patient and the concomitant disorders.
Therapy includes the use of exfoliating, anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative and immunosuppressive drugs. With the use of these agents, the desired effect occurs, the skin is smoothed and the papules disappear. Approximately 70% of patients respond favorably to phototherapy. In the treatment of the disease, balneotherapy, keratolytic (salicylates, urea), corticosteroids, tar, vitamin A and D 3 derivatives.