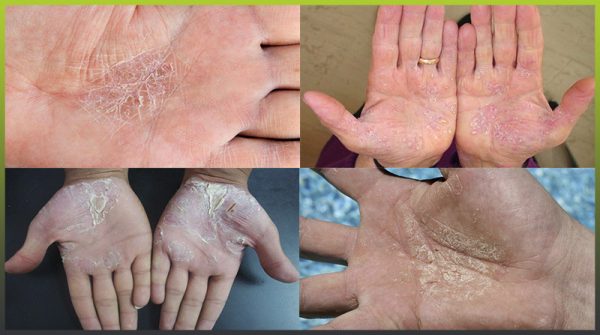
Psoriasis on the hands is one of the serious autoimmune diseases having skin manifestations. If psoriasis is not treated, it can later affect the joints. Most often the disease manifests itself at 15-35 years of age and also after 60 years of age.
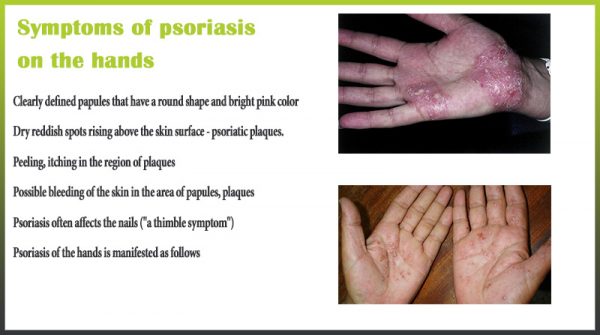
Symptoms of psoriasis on the hands
The signs of psoriasis on the fingers and palms appear suddenly. At first, there are small rashes which later turn into large lesions. Manifestations of psoriasis on the hands:
- Clearly defined papules that have a round shape and bright pink color.
- Dry reddish spots rising above the skin surface – psoriatic plaques.
- Peeling, itching in the region of plaques.
- Possible bleeding of the skin in the area of papules, plaques.
- Psoriasis often affects the nails (“a thimble symptom”) – small points appear, the nail plate begins to flake off.
- Psoriasis of the hands is manifested as follows: the rash starts on the back of the palm, between the fingers and on top of them.
The danger of psoriasis on the hands is that it can turn into severe form – psoriatic arthritis. This disease affects the joints, which leads to swelling of the palms, their deformation, violation of extension – flexion function.
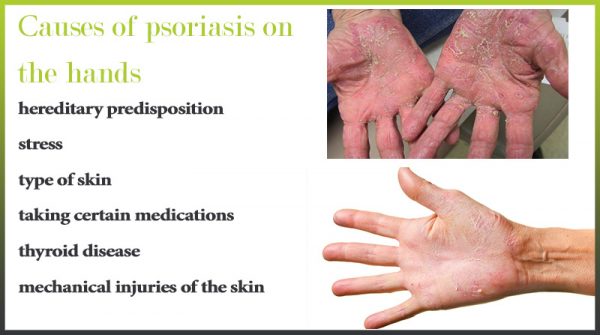
The causes of psoriasis on the hands
Te exact cause of the appearance of psoriasis on the fingers, palms or other parts of the body has not been yet detected. However, medical research could find out the following risk factors for the development of the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- stress;
- type of skin – it was found that people with dry skin type are the ones most often affected by psoriasis;
- taking certain medications, for example, anticonvulsants, sedatives, antidepressants;
- thyroid disease;
- mechanical injuries of the skin – cuts, scratches, etc.
The increased risk of the development of psoriasis refers to people who: smoke, abuse alcohol; have excess body weight; malnourished people.
Stages of the disease
The following stages can be identified: aggravation is a progressive stage of the disease. It is characterized by an increase in the number and size of spots, increased itching and flaking.
Stationary stage – it is characterized by the attenuation of the disease, change in the color of psoriatic plaques (they become less red, whiten), as well as reduction of spots.
The stage of remission is characterized by complete disappearance of all the signs of psoriasis.
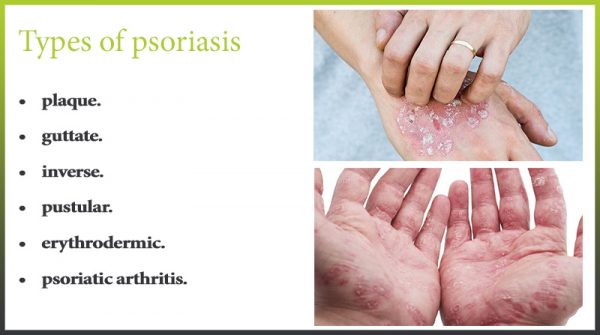
Types of psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis of the hands:
Pustular psoriasis – most often localized on the palms, forearms. With this type of psoriasis, the person notices red spots with purulent liquid inside. These spots merge, forming so-called purulent lakes. Pustular psoriasis of the palms is the most dangerous form of the disease, as it is often complicated by the extensive edema of the palms, the development of nephropathy, and the appearance of dystrophic phenomena.
Guttate psoriasis – most often formed in the upper part of the arm near the shoulders. Plaques resemble drops.
Plaque psoriasis – the plaques join into groups and cover with white crusts.
Psoriasis of the nails – the appearance of longitudinal or transverse lines of gray or white color; thickening of the skin around the nail; loosening and destruction of the entire nail plate.
Localization of psoriasis on the palms: Redness of the skin of the palms, itching, coarsening of the upper layer, the appearance of calluses. Palmar psoriasis is often confused with mycosis or eczema. To make correct diagnosis, one needs to consult a specialist.
Localization on the hands and fingers: Inflammation, puffiness of the fingers, peeling, cracking of the skin, soreness and itching.
Home treatment for psoriasis on hands
Dangers of self-treatment: despite the fact that many medications for the treatment of psoriasis can be bought without a prescription, they can be used only after the approval of a doctor. Otherwise, the consequences can be irreversible:
- psoriasis on the fingers of the fingers – hypercalcemia – occurs when using some ointments, topical creams. This condition can lead to heart rhythm disturbances and even to muscle cramps;
- skin burn – using local remedies, as well as using such method of treatment as phototherapy may lead to skin burn;
- syndrome of addiction, withdrawal;
- occurrence of inflammatory reactions;
- various violations of the endocrine, cardiovascular system – when using hormonal drugs;
- pigmentation of the surrounding healthy skin – coloring in brown;
- occurrence of skin atrophy;
- frequent relapses of the disease, aggravation of the disease.
It is extremely unsafe to use any methods, preparations for the treatment of psoriasis without doctor’s advice on the frequency and duration of application, the area of application of ointment, cream, and without taking into account the individual characteristics of the body!
Without knowing how to treat psoriasis, one can easily harm other organs and systems. Secondly, the person risks to significantly aggravate the course of the disease. And, thirdly, in the absence of adequate treatment, the disease can turn into severe form – it will be very difficult to get rid of it.
One specific rash or scaly plaques appear, one should immediately contact dermatologist.
Topical medications
Every year, the tactics of treating this non-infectious disease are changing. Cytostatics that have side effects have been replaced by non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs and aromatic retinoids, whose objective is to exfoliate dead skin cells, remove inflammation, prevent the formation of psoriatic plaques, and the process of skin keratinizing. For local therapy, various creams and ointments with vitamins A and D are used.
Hand creams for psoriasis
The creams for this disease can be:
Hormonal – they suppress the immune response and reduce the intensity of metabolic processes in the affected skin cells. If the composition of these creams also includes vasoconstrictor substances, then they are twice more effective, as when the drug is applied to the skin, the process of reducing the concentration of nutrients takes place, the process of exfoliating the skin normalizes.
Non-hormonal – they have a pronounced moisturizing effect. In comparison with hormonal creams, these do not cause dangerous side effects, do not lead to a violation of the hormonal balance, and they are way more affordable in terms of prices.
The intake of oral medications
In addition to local agents, the patients suffering from psoriasis are given oral medications:
Antihistamines are used to eliminate severe itching, which is especially strong at night.
Monoclonal antibodies are the antibodies to inflammatory factors. These are substances that “tag” the cells that cause psoriasis, and these cells are later destroyed by immunity. This method of treatment is used only in severe forms of psoriasis. The antibodies are injected intramuscularly.
Cytostatic drugs that are involved in the pathogenesis of the formation of psoriatic plaques.
Preparations of cyclosporine group which have an immunosuppressive effect.
Immunomodulators, vitamin preparations.
Anti-inflammatory drugs – “Metoject” pills, etc. They inhibit the growth of plaques, relieve inflammation.
Homeopathic medications.
Sedatives – they normalize the psychoemotional state.
Traditional herbs
Sea salt – baths with sea salt help to remove inflammation, itching, cleanse the skin of crusts and scales. It is necessary to dissolve a handful of sea salt in 2 liters of warm water. Put your hands in the container, the time of taking the bath can last for 20 minutes.
Flaxseed oil or sea buckthorn oil – restores the skin, prevents dryness, protects against penetration of various infections under the epidermis, saturates the skin with vitamins A and E.
Aloe – has an antiseptic effect. Cut aloe leaf in a half, put it on the problem area on the arm, tie it with adhesive tape or wrap it around with a bandage. Keep for 20 to 30 minutes.
The treatment of this disease needs to be carried out only under close supervision of a dermatologist. Only methods and means that the doctor prescribes to a specific patient can be used.