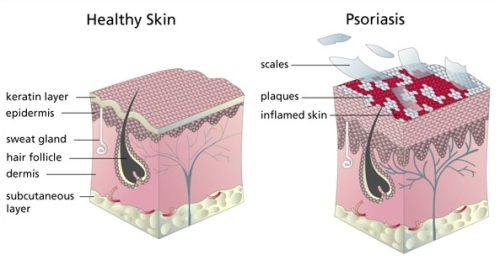
Psoriasis is a chronic disease of skin that results in thick, white, red or silver patches on the skin due to quick growth of the skin cells.
The normal skin cells grow slowly and then tend to flake off within 4 weeks which are then replaced by outer skin layers that get shed off. But in case of psoriasis, the cells grow faster with the above mechanism being repeated in day instead of weeks. This results in formation of plaques or thick patches. Psoriasis is seen commonly in adults between ages of 15 to 35 years but may also occur in children and teens. Prevalence of psoriasis is 2-4% in general population and 1.3-2.2% in UK.
Causes of Psoriasis
There is no single cause identified till date for the occurrence of psoriasis. It is believed that psoriasis occurs due to overactive immune system or autoimmunity that leads to flaking as well as inflammation of the skin. Genetics may be another cause of psoriasis as it may be seen in families. Environmental agents may also be one of the predisposing agents as well as triggering agents for psoriasis.
Signs and symptoms of Psoriasis
The psoriatic signs and symptoms may occur in different intensities and frequencies. Psoriasis could be mild, with small patches of inflammation or rash on skin. In case ofmoderate to severe psoriasis, there is inflammation with raised red patches capped with loose, silvery white, scaly skin. In severe psoriasis, the skin becomes itchy as well as tender. Sometimes large plaques form on the skin that may become uncomfortable. These plaques or large patches may cluster together and cover large region of skin, such as the entire back. Psoriasis affects the elbows, knees, skin folds, nails and scalp.
Is Psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious as it does not pass from one individual to other.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Most of the times, doctors may diagnose psoriasis by simply looking at the patches on the skin, scalp, or nails. Special tests aren’t required for diagnosing psoriasis.Sometimes, blood tests, X-rays or biopsies may be performed in order to rule out the other possible skin diseases.
Prevention of Psoriasis
Most of the cases of psoriasis are mid that can be prevented with appropriate skin care. Various skin care home measures can help in prevention or control of psoriasis. Follow are some tips to care for psoriasis:
- Use moisturizing creams or lotions regularly to avoid dryness. One should also prefer using special moisturizing baths or soaks to keep their skin moist.
- Try to shorten exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light or direct sunlight.
- Aloe vera might be another good option which is available in form of gels and creams. One should follow the instructions carefully while using the skin products or the other prescribed medicines.
- Avoid using the skin products which cause dryness or other adverse effects on skin.
Treatment of Psoriasis
Although psoriasis cannot be completely cured, but some of the cases of psoriasis can be treated with the following treatment measures:
- Moisturizing the skin using various creams, ointments, and lotions. These products should be used after consulting the doctor in order to avoid any side effects.
- Using appropriate shampoos, oils, or sprays as per the doctor’s directions, in order to treat psoriasis in the scalp.
- Appropriate exposure to sunlight (neither more nor less)
- Medications or pills prescribed by your doctor.
- Supplements to help improvise your immune system.
- Phototherapy, which includes exposing the affected regions of skin to special ultraviolet light.
- Dealing with stress in order to improvise immunity.
Medications for Psoriasis
Different medications can be prescribed depending upon the severity of psoriasis:
- For mild cases, psoriasis may be controlled using over-the-counter medicines like corticosteroid creams.
- For moderate to severe cases, topical medicines includingcorticosteroid creams or medicines containing vitamin D such as calcipotriene can be taken, as prescribed by the doctor. Anthralin and tars are some other topical medicines which can be applied in case of psoriasis.
- Occlusion therapy
- Biologics:These are similar to the proteins produce by the body. These biologics work by blocking the adverse response of the immune system of the body and prevents from causing signs of psoriasis.